What you eat can influence glaucoma progression. Glaucoma, a condition affecting the optic nerve, is tied to factors like high intraocular pressure (IOP), oxidative stress, and poor blood flow. While medical treatments like medications or surgery are essential, diet can play a supporting role by addressing these contributing factors. Key points include:
- Foods to Avoid: High-fat diets, refined carbs, excessive salt, and caffeine may worsen glaucoma by increasing IOP, triggering inflammation, or reducing blood flow to the optic nerve.
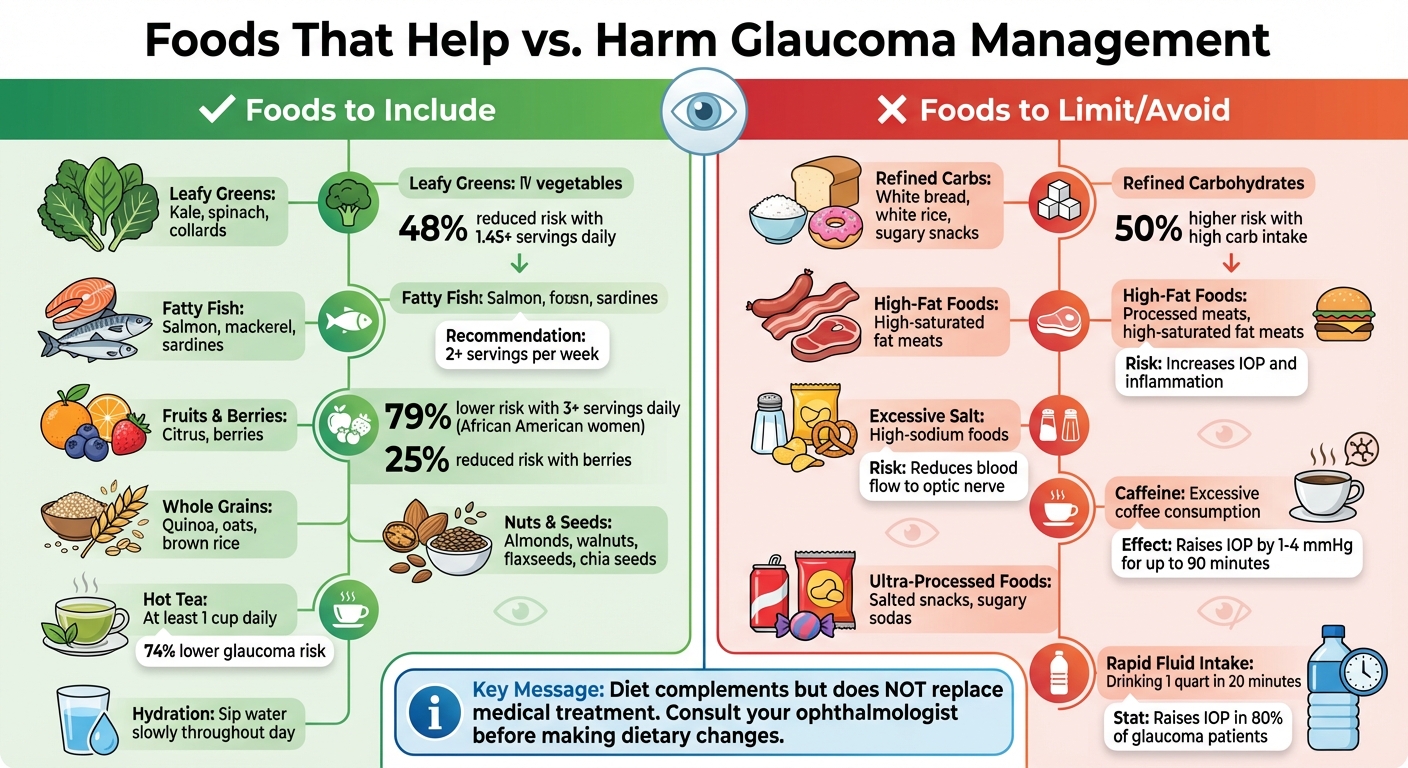
- Foods to Include: Leafy greens (rich in nitrates), fatty fish (omega-3s), fruits, whole grains, and antioxidant-rich foods like nuts and berries can help protect eye health.
- Hydration Tips: Sip water throughout the day instead of consuming large amounts quickly, which can spike IOP.
Diet alone won’t cure glaucoma but can complement traditional treatments. Regular eye exams and professional care remain essential for managing this condition.
Glaucoma Diet and Lifestyle Changes That Can Help!
Foods and Diets That May Worsen Glaucoma
While some foods and dietary habits promote eye health, others can aggravate glaucoma. Certain eating patterns can increase intraocular pressure (IOP), trigger inflammation, or speed up nerve damage – factors that can worsen the condition.
High-Fat and High-Calorie Diets
Diets loaded with fat and calories can lead to obesity, which raises BMI and increases orbital fat. This added fat can block the drainage of aqueous humor, causing a rise in IOP. Obesity is also linked to oxidative stress and systemic inflammation, both of which harm the trabecular meshwork and make glaucoma worse.
High carbohydrate consumption is another concern. Studies indicate that individuals consuming the most carbohydrates have a 50% higher risk of glaucoma compared to those with lower intake. Refined carbs like white bread, white rice, and sugary snacks spike blood sugar levels, leading to metabolic issues that are associated with elevated IOP.
Too Much Salt and Caffeine
Excessive salt in the diet can harm blood vessels and reduce the flow of blood to the optic nerve. Sodium stiffens endothelial cells in blood vessels and limits nitric oxide production, a compound essential for maintaining healthy blood flow. This vascular stress can lead to oxidative damage, which may cause optic nerve cells to die.
"Urinary sodium excretion, a biological indicator of dietary sodium intake, may be a key and modifiable risk factor for the development of glaucoma, especially in those individuals with a higher genetic susceptibility." – Yuqi Yang et al., Department of Ophthalmology, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University
Caffeine also affects eye pressure. Acting as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, caffeine increases the production of aqueous humor in the eye. Drinking a single cup of coffee can raise IOP by 1–4 mmHg for up to 90 minutes. For people with glaucoma – or those predisposed to it – this temporary spike can be problematic. Heavy coffee consumption has been linked to pseudoexfoliative glaucoma, potentially due to its impact on homocysteine levels.
Another factor to consider is rapid fluid intake. Consuming a quart of water within 20 minutes can raise IOP in about 80% of people with glaucoma, compared to just 20% of those without the condition. This underscores how sensitive glaucomatous eyes are to sudden shifts in fluid balance.
Understanding these dietary risks provides a foundation for exploring foods and diets that can help protect eye health.
Diets and Nutrients That Support Eye Health
Mediterranean Diet and Plant-Based Eating
Some eating habits and nutrients can actively promote eye health, offering protection against conditions like glaucoma. The Mediterranean diet – featuring fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fatty fish, nuts, and extra virgin olive oil – is particularly beneficial. This diet helps protect against glaucoma by increasing nitric oxide levels, reducing oxidative stress, and lowering intraocular pressure. Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties directly address the oxidative stress and inflammation that can harm the optic nerve.
Green leafy vegetables, packed with nitrates, play a key role in regulating intraocular pressure and enhancing blood flow to the optic nerve. Research shows that consuming at least 1.45 servings of leafy greens daily can reduce glaucoma risk by 48%. Additionally, African American women who eat three or more servings of fruits or fruit juices per day are 79% less likely to develop glaucoma compared to those consuming less than one serving.
Drinking hot tea also appears to have protective benefits. Studies link drinking at least one cup of hot tea daily with a 74% lower risk of glaucoma compared to non-tea drinkers. Adding berries to your diet may further reduce glaucoma risk by up to 25%.
These dietary choices provide a strong foundation for more targeted nutrient-based strategies to manage glaucoma.
Key Nutrients for Glaucoma Management
Certain nutrients are especially effective in slowing glaucoma progression and protecting eye health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, improve blood flow to the eyes and help lower intraocular pressure. Aim to include at least two servings of fatty fish in your diet each week.
Antioxidants, including vitamins A, C, and E, are essential for neutralizing free radicals that can damage eye cells. Vitamin C helps protect cell membranes, while Vitamin E combats oxidative damage caused by lipid peroxidation. Foods like citrus fruits, berries, nuts, and seeds are excellent sources of these antioxidants. Additionally, magnesium – found in nuts, seeds, and leafy greens – acts as a natural calcium channel blocker, improving blood flow to the eyes and protecting retinal ganglion cells.
"Antioxidants play an important role in preventing and mitigating glaucoma, effectively reducing the negative effects of oxidative stress on eye health." – Yuqi Yang, Department of Ophthalmology, China-Japan Union Hospital
Switching from refined grains to whole grains such as quinoa, oats, and brown rice can also be beneficial. Whole grains retain fiber and antioxidants that support stable blood sugar levels – a key factor in reducing glaucoma risk – and promote cardiovascular health. For plant-based omega-3s, consider adding walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds to your meals.
These nutrient-rich foods and dietary adjustments can make a meaningful difference in protecting your vision and managing glaucoma.
sbb-itb-c87b093
Practical Dietary Strategies for Managing Glaucoma
Glaucoma Diet Guide: Protective vs High-Risk Foods Comparison
Turning nutrient recommendations into everyday habits can make managing glaucoma more practical and effective.
Hydration and Meal Timing Tips
How you hydrate can influence eye pressure. For instance, drinking a full quart of water in a short span – like 20 minutes – can raise eye pressure in 80% of glaucoma patients. To avoid this, sip water in small amounts consistently throughout the day to help maintain steady eye pressure. Similarly, meal timing plays a role. Instead of large meals that might elevate intraocular pressure, aim for smaller, well-balanced portions spaced evenly throughout the day.
If you’re a coffee drinker, consider moderating your caffeine intake. Swapping some servings for decaffeinated coffee or hot tea can help. Dr. Yvonne Ou, MD, Professor of Ophthalmology at the University of California, San Francisco, advises:
"A good rule of thumb is to exercise moderation with caffeine consumption. One cup of coffee is unlikely to cause any harm, but if you like to drink large amounts of coffee consider switching some of that consumption to decaffeinated".
High-Risk vs. Protective Foods Comparison
Making smart food swaps can support better eye health. For instance, replace refined grains like white rice or bread with whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, or whole wheat pasta to promote cardiovascular health and stabilize blood sugar. When it comes to leafy greens, add tender options like baby spinach or arugula raw to salads and wraps, while heartier greens like collards can be sautéed with garlic and olive oil for a flavorful side. Incorporating fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, or sardines into your meals at least twice a week is another great step. Opt for baking, grilling, or steaming to preserve nutrients.
Here’s a quick comparison of protective and high-risk foods:
| Food Category | Protective Foods | High-Risk Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Proteins | Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), black beans | Processed meats, high-saturated fat meats |
| Grains | Whole grains (oats, quinoa, brown rice) | Refined grains (white bread, white rice) |
| Snacks | Nuts (almonds, hazelnuts), seeds, dark chocolate | Ultra-processed foods, salted snacks |
| Beverages | Hot tea, water (small amounts) | Excessive caffeine, heavy alcohol, sugary sodas |
| Fats | Vegetable fats, Omega-3 rich oils | Trans fats, high-saturated fats |
For quick and healthy meals, consider using pre-cooked multigrain rice packets as a base for stir-fries or grain bowls. Snack on a handful of mixed nuts or sprinkle them over salads for added crunch. Fresh fruits like berries or citrus can easily be blended into smoothies or added to yogurt bowls for a boost of flavor and nutrients. When washing greens, use running water to preserve their nutritional value.
Combining Diet with Professional Glaucoma Care
While good nutrition plays a role in supporting eye health, it works best when paired with professional medical care. It’s important to note that nutrition alone cannot cure glaucoma or stop its progression. The only proven methods to manage this condition and prevent permanent vision loss involve lowering intraocular pressure through medications, laser therapy, or surgery. Dr. Adi M. Al Owaifeer from King Faisal University‘s Faculty of Ophthalmology puts it plainly:
"Nutritional management may complement, but would not substitute conventional glaucoma treatment".
Think of diet as a helpful addition to your treatment plan, not a replacement. These healthy practices are most effective when they work alongside your prescribed care. Regular, thorough eye exams are critical for tracking intraocular pressure and monitoring changes to the optic nerve. Without professional oversight, even well-intentioned habits could have unintended consequences.
Before introducing supplements into your routine, talk to your ophthalmologist. Some herbal remedies, such as Ginkgo biloba, may interfere with medications or increase the risk of complications during surgery. Even vitamins and minerals, when taken in excessive amounts, can lead to serious health problems. Consulting with an eye care specialist ensures that your dietary choices align with your treatment plan and don’t inadvertently cause harm.
Why Consult Boulder Eye Surgeons?
Pairing professional expertise with smart lifestyle choices can make a big difference in managing glaucoma. Boulder Eye Surgeons offers comprehensive glaucoma care, utilizing advanced technology and personalized treatment plans. Located in Boulder, CO, and serving the surrounding areas, their team specializes in both glaucoma and cataract surgery. By combining cutting-edge research with practical clinical care, they provide evidence-based treatments while offering guidance on how safe lifestyle changes, including dietary adjustments, can support your vision health.
From medical management to advanced surgical options, Boulder Eye Surgeons delivers the full range of care needed to effectively manage glaucoma. Their approach includes regular monitoring, tailored treatment plans, and expert advice on integrating nutrition into your overall care. Schedule a consultation to learn how professional glaucoma care, combined with thoughtful dietary choices, can help protect your vision for the long term.
Conclusion: Diet’s Role in Glaucoma Management
What you eat plays a crucial role in managing glaucoma, though it’s not a standalone solution. A diet packed with leafy greens, fatty fish, berries, and whole grains can promote eye health by helping regulate intraocular pressure, boosting blood flow, and supplying antioxidants. For instance, studies show that regularly eating kale and spinach can reduce the risk of developing glaucoma by 20% to 30%. Similarly, drinking at least one cup of hot tea daily has been associated with a remarkable 74% lower risk of being diagnosed with the condition.
On the flip side, certain dietary habits can make glaucoma worse. Diets high in carbohydrates, excessive salt, and ultra-processed foods may contribute to disease progression by negatively affecting blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and vascular health.
It’s important to remember that while diet can support glaucoma management, it’s not a replacement for medical care. Dietary adjustments should be viewed as a complement to proven treatments like medications, laser therapy, or surgery. Regular monitoring and professional medical interventions remain essential to prevent vision loss.
FAQs
Can changing your diet help manage glaucoma?
While dietary changes alone can’t control glaucoma, they can support overall eye health and may help slow the disease’s progression. Pairing a nutritious diet with the treatments recommended by your eye doctor is key to managing glaucoma effectively.
Adding antioxidant-rich foods like leafy greens, berries, and citrus fruits into your meals can be helpful. Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish such as salmon and tuna, are also thought to promote eye health. On the other hand, cutting back on excessive salt and caffeine might help lower eye pressure. For advice tailored to your specific needs, always consult your doctor.
What foods are best for supporting eye health in glaucoma patients?
A nutrient-packed diet can play a supportive role in managing glaucoma and promoting overall eye health. Start by adding leafy greens like kale, spinach, and collard greens to your meals. These are rich in nitrates, which may enhance blood flow to the optic nerve. Additionally, include fruits and vegetables high in antioxidants, such as carrots, peaches, and radishes, to help combat oxidative stress linked to glaucoma progression.
For more antioxidant power, consider incorporating berries like blueberries and cranberries, dark chocolate, and green tea into your diet. These foods help protect retinal tissues from damage. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in salmon and walnuts, along with minerals like magnesium and zinc, are also important for maintaining healthy eyes. While a balanced diet won’t replace medical treatments, it can work alongside them to support better glaucoma management.
Can drinking caffeine affect eye pressure in people with glaucoma?
Caffeine has been shown to cause a temporary increase in intraocular pressure (IOP), with the effects lasting for up to 90 minutes. For most people, moderate caffeine consumption – like enjoying a single cup of coffee – is not a problem. However, if you have glaucoma or are at risk, drinking excessive amounts of caffeine could be more concerning. If caffeine is a regular part of your routine, it’s a good idea to talk to your doctor about how it might affect your eye health.